|
Tokyo Metro 07 Series
The is an electric multiple unit (EMU) train type operated by Tokyo Metro in Tokyo, Japan. Introduced into service in 1993, a total of six 10-car sets were manufactured by Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Nippon Sharyo between 1993 and 1994 for use on the Tokyo Metro Yūrakuchō Line. From 2006, the sets were permanently transferred to the Tokyo Metro Tōzai Line to replace ageing 5000 series trainsets. Operations Current * Tokyo Metro Tōzai Line * Tōyō Rapid Line between Nishi-Funabashi Station and Tōyō-Katsutadai Station * JR Chūō-Sōbu Line between Nakano Station and Mitaka Station * JR Chūō-Sōbu Line between Nishi-Funabashi Station and Tsudanuma Station (weekday mornings and evenings only) Former * Tokyo Metro Yurakucho Line between Wakōshi and Shin-Kiba (from 1992 until 2008); during that period the 07 series EMUs also inter-ran into the Tobu Tojo Line to Kawagoeshi and on the Seibu Yūrakuchō Line and Seibu Ikebukuro Line to Hannō Station via Nerima S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Heavy Industries Rolling Stock Company
is the rolling stock manufacturing subsidiary of Kawasaki Heavy Industries. Since beginning operations in 1906, the company has produced more than 90,000 railroad cars. Products As indicated by the company name, the company mainly produces railroad vehicles. Recently Kawasaki has received orders from customers in foreign countries, including Ireland and the United States. All products manufactured for the US rail market are sold through Kawasaki Rail Car Inc., another division of Kawasaki Heavy Industries. An assembly plant in Lincoln, Nebraska produces fully completed cars and "knocked down" cars. Because of substantial sales to the New York City Subway and various commuter lines, an additional assembly plant was established in Yonkers, New York in 1986 for final assembly of cars built in Lincoln. In November 2020, Kawasaki Heavy Industries announced that it would spin off some of its businesses, including the rolling stock division from October 2021. Japan Railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronically Controlled Pneumatic Brakes
Electronically controlled pneumatic brakes are a type of modern railway braking system which offer improved performance compared to traditional railway air brakes. Overview Traditional train braking systems use pneumatic valves to control and generate brake applications on the cars along the length of the train. In general, this conventional system consists of a brake pipe that runs the length of the train which supplies air to reservoirs mounted on each of the cars. When the brake pipe and car components are charged with air, the brakes release. When the engineer needs to make a brake application, control valves in the locomotive reduce the brake pipe pressure. As the brake pipe pressure reduces, the service portion on each car diverts air from their reservoirs to their brake cylinders. To release the brakes, the engineer charges the brake pipe. This method of controlling the brakes on freight and passenger cars has remained virtually unchanged since its invention by George Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsudanuma Station
is a junction passenger railway station located in the city of Narashino, Chiba, Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). Lines Tsudanuma Station is served by the Sōbu Main Line ( rapid service and local service). It is 26.7 kilometers from the starting point of both lines at Tokyo Station. Station layout Tsudanuma Station consists of three island platforms serving six tracks, with an elevated station building. The station has a ''Midori no Madoguchi'' staffed ticket office. Platforms History The station opened on September 21, 1895. Passenger statistics In fiscal 2019, the station was used by an average of 102,846 passengers daily (boarding passengers only). The daily passenger figures (boarding passengers only) in previous years are as shown below. Surrounding area * Shin-Tsudanuma Station ( Shin-Keisei Line) * Chiba Institute of Technology See also * List of railway stations in Japan The links below contain all of the 8579 railway stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitaka Station
is a passenger railway station located in the city of Mitaka, Tokyo, Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). Lines Mitaka Station is served by the Chūō Main Line, acting as the terminus for all-stations Chūō-Sōbu Line services from , with Chūō Line (Rapid) limited stop services from . Some Tokyo Metro Tōzai Line inter-running services also originate and terminate here. The station is 24.1 kilometers from Tokyo Station. Station layout The station comprises three island platforms serving six tracks, with the station building located above and perpendicular to the platforms. The station has a "Midori no Madoguchi" staffed ticket office. Platforms History Mitaka Station opened on 25 June 1930. On 15 July 1949, an unmanned train, with its controls tied down, crashed into the station, killing 6 and injuring 20. The incident remains shrouded in mystery. Passenger statistics In fiscal 2019, the JR station was used by an average of 98,796 passengers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakano Station (Tokyo)
is a railway station on the Chūō Main Line in Nakano, Tokyo in Japan, operated jointly by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and the Tokyo subway operator Tokyo Metro. Lines Nakano Station is served by the JR East Chuo Line (Rapid) and Chuo-Sobu Line, and the Tokyo Metro Tozai Line. There are no turnstiles between lines, allowing for easy transfers. Station layout The station consists of four island platforms serving eight tracks. Platforms File:JR Chuo-Main-Line・Tokyo Metro Tozai-Line Nakano Station Platform 1・2 (20210418).jpg, Platforms 1 and 2 (April 2021) File:JR Chuo-Main-Line・Tokyo Metro Tozai-Line Nakano Station Platform 3・4 (20210418).jpg, Platforms 3 and 4 (April 2021) File:JR Chuo-Main-Line・Tokyo Metro Tozai-Line Nakano Station Platform 5・6.jpg, Platforms 5 and 6 File:JR Chuo-Main-Line・Tokyo Metro Tozai-Line Nakano Station Platform 7・8.jpg, Platforms 7 and 8 File:TokyoMetro-T01-Nakano-station-sign-20210120-115814.jpg, Station sign Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tōyō-Katsutadai Station
is a passenger railway station in the city of Yachiyo, Chiba, Japan, operated by the third sector railway operator Tōyō Rapid Railway. Lines Tōyō-Katsutadai Station is a terminus of the Tōyō Rapid Railway Line, and is 16.2 km from the opposing terminus of the line at Nishi-Funabashi Station. Station layout The station is an underground station with a single island platform serving two tracks, located on the second basement level. The ticket barriers are on the first basement level. Platforms History Tōyō-Katsutadai Station was opened on April 27, 1996. In 1997, an underground passage was built to the nearby Keisei Main Line Katsutadai Station. Passenger statistics In fiscal 2018, the station was used by an average of 31,927 passengers daily. Surrounding area * Tōyō-Katsutadai bus terminal * Yachiyodai High School See also * List of railway stations in Japan The links below contain all of the 8579 railway stations in Japan. External links {{Portal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishi-Funabashi Station
is a railway station in Funabashi, Japan, operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East), Tokyo Metro, and the Tōyō Rapid Railway. It is the easternmost station of the Tokyo subway network, lying in Chiba Prefecture. Lines Nishi-Funabashi Station is served by the following lines. *East Japan Railway Company **Chūō-Sōbu Line **Musashino Line **Keiyō Line *Tokyo Metro **Tokyo Metro Tōzai Line, Tōzai Line *Tōyō Rapid Railway **Tōyō Rapid Railway Line Station layout The station consists of six island platforms serving eleven tracks on two levels (another two tracks are used by Sōbu Line (Rapid) trains which do not stop at the station). The high-level station serves the Keiyō Line, Keiyō and Musashino Lines. The low level is served by the Chūō-Sōbu Line, Sōbu, Tokyo Metro Tōzai Line, Tōzai and Tōyō Rapid Railway Lines. The low level can be subdivided into two sections, one served by trains running into Tokyo via the Sōbu Line and the other by trains runnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Metro Yūrakuchō Line
The is a subway line in Japan owned and operated by Tokyo Metro. The line connects Wakōshi Station in Wakō, Saitama and Shin-Kiba Station in Kōtō, Tokyo. On maps, diagrams and signboards, the line is shown using the color "gold" (), and its stations are given numbers using the letter "Y". The line was named after the Yūrakuchō business district in Chiyoda, Tokyo. The proper name as given in an annual report of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport is . According to the Tokyo urban transportation plan, however, it is more complicated. The line number assigned to the section south from Kotake-Mukaihara to Shin-Kiba is Line 8, but that north of Kotake-Mukaihara to Wakōshi is Line 13, which indicates the section is a portion of Fukutoshin Line which shares the same number. Services The Yurakucho Line has inter-running counterparts on its northern side, both of which are "major" Japanese private railway companies in Greater Tokyo. One is the Tobu Railway at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
(or simply Kawasaki) is a Japanese Public company, public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, Heavy equipment (construction), heavy equipment, aerospace and Military, defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headquartered in Chūō-ku, Kobe, Chūō, Kobe and Minato, Tokyo, Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It is also active in the production of industrial robots, gas turbines, pumps, boilers and other industrial products. The company is named after its founder, Kawasaki Shōzō, Shōzō Kawasaki. KHI is known as one of the three major heavy industrial manufacturers of Japan, alongside Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and IHI Corporation, IHI. Prior to the World War II, Second World War, KHI was part of the Kobe Kawasaki ''zaibatsu'', which included JFE Holdings, Kawasaki Steel and K Line, Kawasaki Kisen. After the conflict, KHI became part of the DKB Group (''keiretsu''). History Kawasaki Shōzō, Shōzō Kawasaki, born in 1836, was involved with the marine indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Multiple Unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number of the carriages. An EMU is usually formed of two or more semi-permanently coupled carriages, but electrically powered single-unit railcars are also generally classed as EMUs. The great majority of EMUs are passenger trains, but versions also exist for carrying mail. EMUs are popular on commuter and suburban rail networks around the world due to their fast acceleration and pollution-free operation. Being quieter than diesel multiple units (DMUs) and locomotive-hauled trains, EMUs can operate later at night and more frequently without disturbing nearby residents. In addition, tunnel design for EMU trains is simpler as no provision is needed for exhausting fumes, although retrofitting existing limited-clearance tunnels to accommodate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Coupling
A coupling (or a coupler) is a mechanism typically placed at each end of a railway vehicle that connects them together to form a train. A variety of coupler types have been developed over the course of railway history. Key issues in their design include strength, reliability, ease of making connections and operator safety. The equipment that connects the couplings to the vehicles is the draft gear or draw gear and these must absorb the stresses of coupling and train acceleration. Nomenclature Compatible and similar couplings or couplers are frequently referred to using widely differing make, brand, or regional names, or nicknames, which can make describing standard or typical designs confusing. Dimensions and ratings noted in these articles are usually of nominal or typical components and systems, though standards and practices also vary widely with railway, region, and era. Buffers and chain The basic type of coupling on railways following the British tradition is the bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
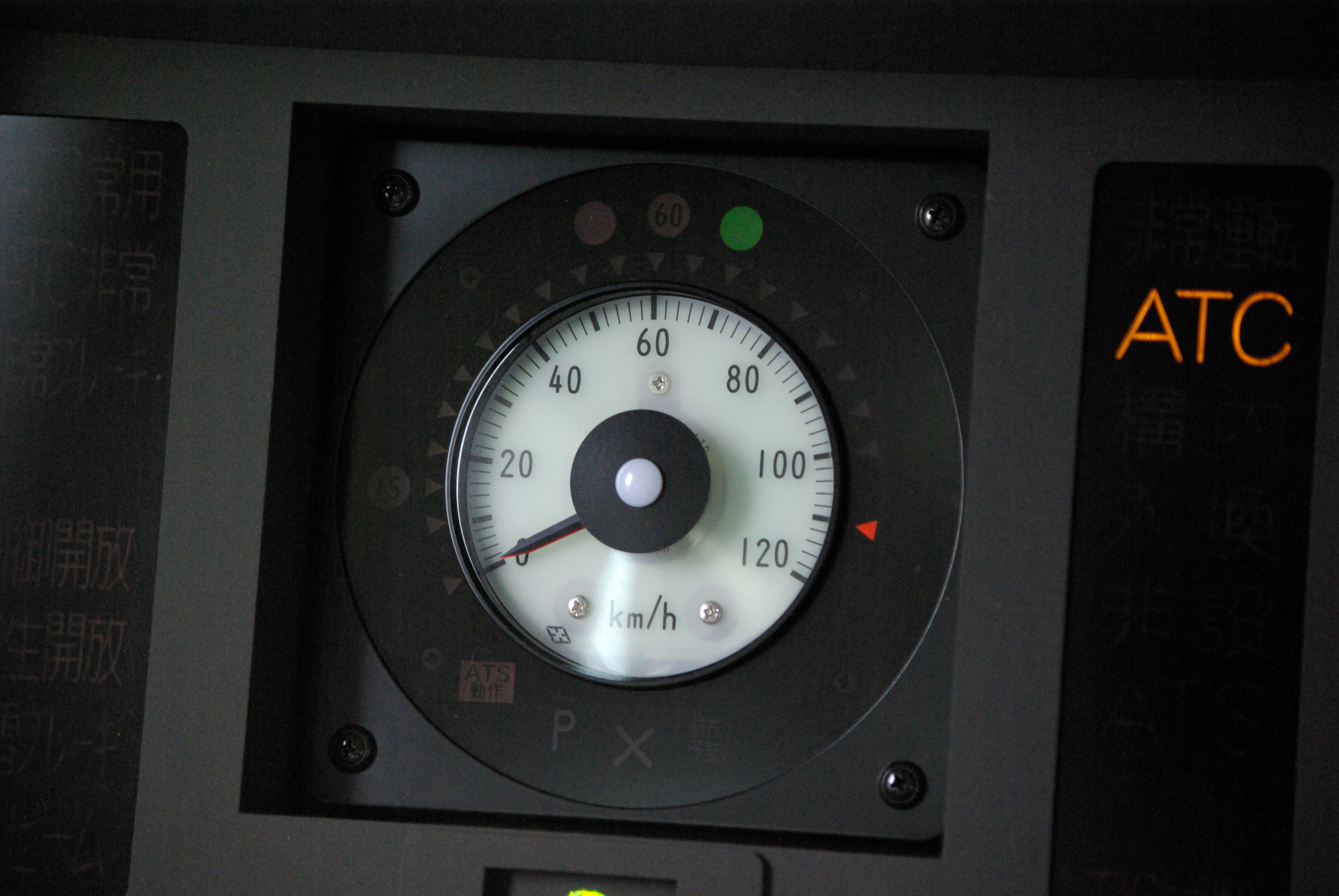
Automatic Train Control
Automatic train control (ATC) is a general class of train protection systems for railways that involves a speed control mechanism in response to external inputs. For example, a system could effect an emergency brake application if the driver does not react to a signal at danger. ATC systems tend to integrate various cab signalling technologies and they use more granular deceleration patterns in lieu of the rigid stops encountered with the older automatic train stop (ATS) technology. ATC can also be used with automatic train operation (ATO) and is usually considered to be the safety-critical part of a railway system. Over time, there have been many different safety systems labelled as "automatic train control". The first experimental apparatus was installed on the Henley branch line in January 1906 by the Great Western Railway, although it would now be referred to as an automatic warning system (AWS) because the driver retained full command of braking. The term is especially co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)